You can use the Database Navigator to:
| · | browse your schema structure
|
| · | browse object dependencies
|
| · | drop schema objects
|
| · | print schema objects
|
| · | open the Object Editors
|
| · | quickly duplicate objects
|
| · | start/stop the session recorder
|
There are numerous other possibilities - each tree-view node has a powerful and context sensitive popup menu that will open up other tools.
Note:
If you disconnect or close the Database Navigator, all connection-related windows will close as well.
Although Database Workbench strives to create an user interface that's the same for all available database engines, there, of course, are differences between engines. Below is a screen shot from three Database Navigators, one for InterBase, one for Microsoft SQL Server and one for Oracle. You can see the differences between, for example, the availability of database objects and single or multiple schemas.
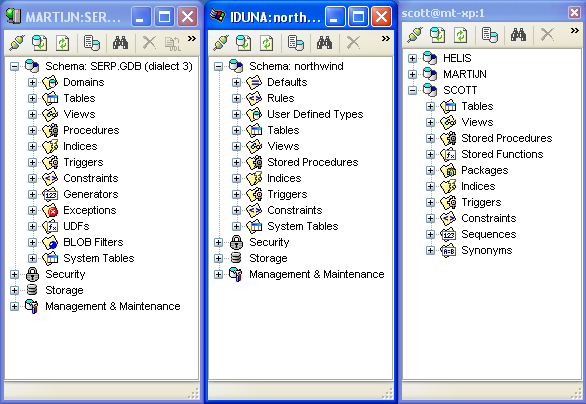
Two Database Navigators - InterBase on the left, MS SQL Server in the middle and Oracle on the right
The tree-view of the Database Navigator can have up to 4 main schema specific tree nodes:
| 1. | Schema (one or more)
|
| 2. | Security
|
| 3. | Storage
|
| 4. | Management & Maintenance
|
If a database engine, like MySQL, doesn't support schema specific security like Roles, the Security node isn't visible.
For detailed information on database engine specific features, see:
| · | Using the Database Navigator with InterBase
|
| · | Using the Database Navigator with Firebird
|
| · | Using the Database Navigator with MS SQL Server
|
| · | Using the Database Navigator with MySQL
|
| · | Using the Database Navigator with Oracle
|
| · | Using the Database Navigator with NexusDB
|
1. Schema
Each Schema node lists a schema (or database) and its objects. These objects are arranged in groups, like Tables and Indices. Indices, for example, are also "child" objects of a table (without a table, there's no index) and are listed as a child node with each table as well. Because each index belongs to a table, the table is also accessible from the index node - therefore creating a recursive tree mechanism.
Almost every node (object type) will have a context sensitive menu, as well as the groups (Tables, Procedure etc). You can use these menus to access commonly used functionality.
Double clicking a group will open the object editor for the group-object type.
You will also notice that for database engines and objects that support user-written descriptions, a "Description" box will be visible - if you select such an object - in the bottom part of the Database Navigator. You can view and modify the description - use the Save Description button to save the description to the database. This box will be displayed automatically, which can be turned OFF in the Preferences.

Description Box
Schema information is cached in Database Workbench, so adding objects via a script or from another workstation will not reflect in the tree view. Either click the Refresh From Database button in the Database Navigator toolbar, or use the context menu of any object group and select Refresh. This will check if any objects have been removed or added.
2. Security
Listed under the Security node is anything related to security that is schema/database specific. This does not include server-wide user accounts, for example. Think of database roles, groups etc.
As usual, the object types are put together in groups. Double clicking the group will open the object editor for that particular object type.
3. Storage
Storage lists the data-files used for the connected schema. Any other groups like "shadows" or "transaction logs" are listed here as well. There are currently no context menus available for anything related to storage.
4. Management & Maintenance
Many different things can be listed under Management & Maintenance - some of which can be found in the Enterprise Manager as well.
The actual functionality listed here is heavily dependent on the type of database engine so better consult the database engine specific topics.